Today, there are more data sources available to us than ever before, and businesses are not an exception. They deal with vast amounts of data, which should be organized effectively to drive valuable insights and streamline operations.
Key Highlights
- Data modeling establishes connections between pieces of information and categorizes them into logical groups, thus elevating data analytics.
- A virtual warehouse offers cloud-based storage, allowing businesses to collect, manage, and analyze data without physical infrastructure.
- By utilizing diagrams, charts, and graphs, data modeling for big data easily generates meaningful insights from massive datasets.
- Agile data modeling helps develop pretty responsive database architectures that can be simply adjusted to changed requirements.
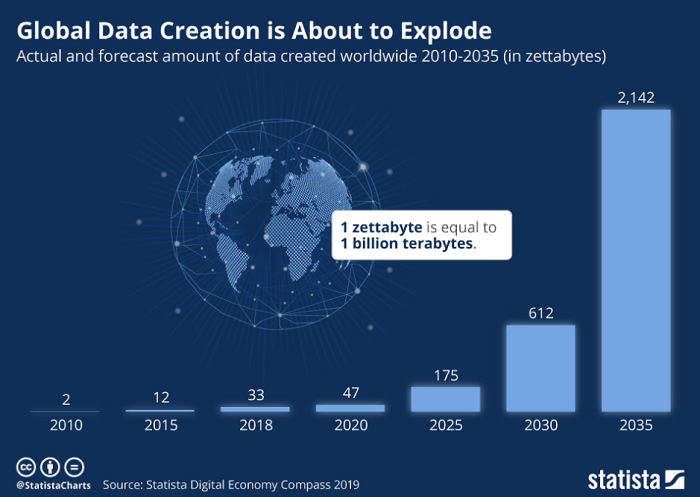
According to Statista, global data creation is projected to grow to 612 zettabytes by 2030 and reach 2140 by 2035. With such an expansion, businesses should focus more on data management if they want to enhance processes and gain a competitive edge in the market. And here, a data modeling strategy can serve as a helping hand to harness data effectively.
Data modeling helps companies structure and organize data by designing a visual representation of it. In essence, it lies at the core of data engineering solutions.
In this blog post, we will take a look at the data modeling techniques, as well as discuss the ways they contribute to efficient data collection, processing, and storage.
What Is Data Modeling?
Data modeling is the process of evaluating and defining different sources and types of data that your company works with. Simply put, it establishes connections between pieces of information and categorizes them into logical groups. That is achieved by creating a visual representation of data with all of its attributes, relationships, and storage locations.
In general, data modeling acts as a well-defined roadmap for data management, helping organizations plan their data architecture more efficiently. On top of that, it supports stakeholders in better decision-making by providing a ground for data analytics and facilitating it.
Discover Types of Data Analytics
Before wrapping up this part, let’s briefly skim through the workflow of the data modeling process to get on the same page about how it exactly functions:
- Identify the entities: Everything starts with assessing what exactly should become an object of modeling.
- Define relationships among entities: Data models, typically, do not include random entities. There should always be a clear relationship between them.
- Normalize variables: Normalization helps ensure there is no repetition in data, thus elevating both redundancy and noticeably optimizing storage.
- Test and validate: To stay efficient and serve the purpose, your data analytics models should be continuously reviewed and updated. Only this way, data models meet changing business goals.
An information model shows what kinds of variables you have in the specific domain. Whereas, data model represents how these variables are structured, stored, and managed in databases.
With this in mind, when comparing an information model vs a data model, the key question to ask is “what” and “how.” The “what” refers to the information model, showing what the relationships between variables are. And “how” applies to data modeling, highlighting the way data is physically organized.
Concepts of Data Modeling
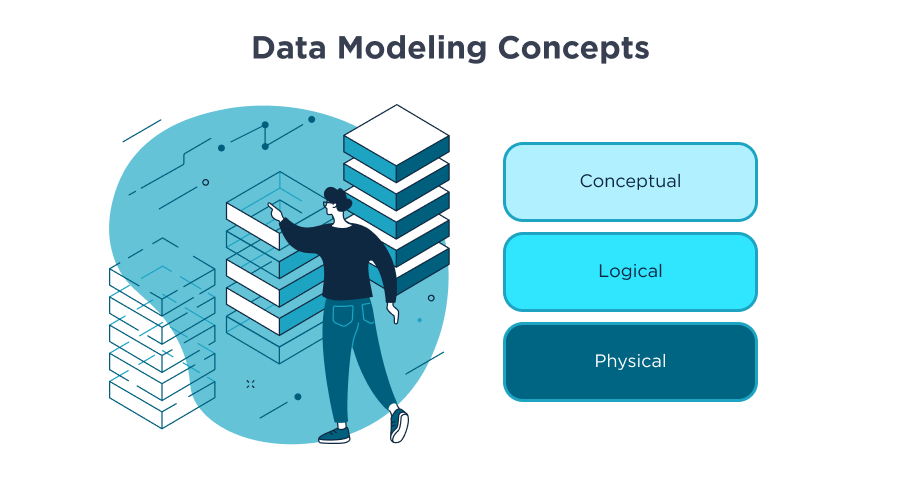
Now, let’s keep diving deeper into the topic and have a look at three main data modeling concepts.
Conceptual: It is typically used at an early stage of the project when we analyze requirements. It provides a high-level overview of what the system will include and how it will be organized.
Logical: This model goes one step further. As the name implies, logical data modeling helps break data into minor logical elements and build a detailed visual schema of relationships between them. It aids organizations in streamlining approaches for data consolidation and segmentation.
Physical: This one derives from a logical concept and helps describe how data will be structured within a specific database management system. It serves as a guide for data engineers during the visualization and implementation of databases.
Common Data Modeling Techniques
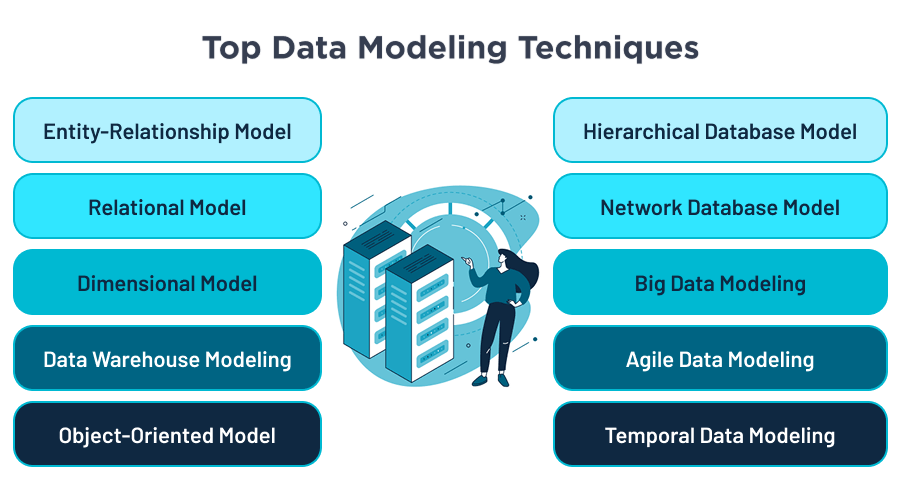
As we’ve already mentioned, when well-structured, a data model serves as a basis for subsequent analysis and informed decision-making. With that in mind, let’s get into the most popular types of data modeling techniques that you can leverage to build an effective data management strategy.
#1 Entity-Relationship (ER) Model
Though introduced in 1976, the entity-relationship data model still remains a thing these days. It illustrates the connections between entities in a database using formal diagrams. They assist in understanding the fundamentals of the information that will be located within the data store.
The ER model contains three main components:
- Entities: Symbolize a real-world entity, such as a person or location, and are displayed on tables.
- Attributes: Explain the features of each entity.
- Relationship: Shows connection between two or more entities that can take several forms, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many.
#2 Relational Model
Another technique that was introduced a long time ago is a relational model. It is still widely used in database architecture, connecting data in tables through rows and columns.
It aims to simplify the data and offer a clear perspective, as well as facilitate efficient storage and analysis. Moreover, it utilizes the principles of set theory and predicate logic.
For example, relational databases can help handle massive amounts of essential customer information, monitor stocks, conduct eCommerce transactions, and much more.
#3 Dimensional Model
Dimensional models are mostly used in data warehouse design with the goal of optimizing a database for faster retrieval of information. They also help remove redundancy and inconsistencies, thus contributing to better data quality.
These models have numerous benefits, including the capacity to organize data for analysis in a simple, clear, and customizable manner. Furthermore, they enable the quick and easy addition of new data, which can support companies with dynamic business environments.
When it comes to optimizing a database, a dimensional model can serve best. That is because it organizes variables in a clear and customizable manner. Thus, allowing access to the needed information right away.
The relational model, on the other hand, connects data in tables through rows and columns, leading to efficient storage and analysis. Data in rows and columns are not placed by chance. Instead, they are all logically related. This significantly elevates and simplifies data analytics.
In a dimensional model, information is divided into two types of tables: fact and dimension. Fact tables are often large and contain millions or billions of rows. For example, they can store data about sales transactions, customer orders, and more.
On the other hand, dimension tables are relatively smaller in size. They contain descriptive information that helps understand data in the context of the business environment.
#4 Data Warehouse Modeling
The next technique in our list is data warehouse modeling. It is the process of building and arranging data models within your data warehouse platform.
Moving forward with the core types of data modeling techniques, let’s talk about warehouse modeling:
Enterprise Warehouse: An enterprise warehouse integrates data from diverse sources. As a result, it reduces data silos and ensures accurate and reliable information throughout the organization. Generally, it comprises both extensive and summary information and can range in size from a few gigabytes to hundreds of gigabytes, terabytes, and even more.
Here, the warehouse serves as a repository for both structured and unstructured data. It helps enterprise software developers use this data to build various solutions for reporting and analysis.
Learn more about Enterprise Warehouse Benefits
Data Mart: The second type of data warehouse modeling is data mart. In simple words, it is a portion of corporate-wide data that is useful to a certain group of users. Overall, it focuses on an exact industry, department, or particular business area.
Take, for instance, marketing data. It can contain data entities such as customers, items, campaigns, sales, and website analytics.
Virtual Warehouse: The third one is a virtual warehouse. It is a cloud-based storage and processing environment where organizations can store, manage, and analyze their data without the need for physical infrastructure. Virtual warehouse takes data management a step further by promoting agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
How to Build a Cloud Data Management Strategy
#5 Object-Oriented Model
Another technique of data modeling is called object-oriented, where data is stored in the form of objects. This model is based on the object-oriented programming approach and involves designing data models that mirror real-world objects and their relationships. Each object has its own set of attributes and behaviors, or methods.
For example, let’s consider a data model for an educational system. In this case, you might have classes like student, teacher, course, and department. Students then could have attributes such as ID, name, major, and a list of enrolled courses. And courses could have attributes like course ID, title, department, and a list of enrolled students, etc.
The object-oriented model is flexible and adaptable since it allows for quick model modification and enhancement as requirements change. Thus, you can benefit from it when you need, let’s say, to add new object types without changing the old ones.
Get the most out of your data with us
LEARN MORE#6 Hierarchical Database Model
This approach organizes data in the form of a tree, maintaining a parent-child relationship within records. A parent can have more than one child, while a child record is limited to having only one parent.
The hierarchical model helps maintain data consistency since changes to a parent record are automatically transmitted to its children. Furthermore, by limiting access to certain levels of the hierarchy, you can gain comprehensive control over data.
#7 Network Database Model
The network model is an expanded version of the hierarchical one. It enables a child record to have one or more parents. When compared to the hierarchical approach, it allows for more flexible data access.
By incorporating the network model technique into the data modeling process, you may capture the intricate relationships and interactions between various data points, enhancing the accuracy of the overall data model.
#8 Big Data Modeling
When it comes to analyzing big data, it’s quite challenging to implement it using traditional methods due to large volumes of data. In order to manage this process smoothly, you can leverage big data modeling.
This technique is tailored to handle the unique characteristics of big data, such as volume, velocity, variety, and variability. By using visual models, like diagrams, charts, and graphs, you can easily generate insights from massive and complicated datasets.
Big data modeling is often empowered by machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies that help businesses comprehend and evaluate vast amounts of data. AI and ML can be used for many purposes, such as automated data collection, making predictions, deriving insights, and so on.
Want to unleash the power of AI technologies?
TALK TO US#9 Agile Data Modeling
As the name suggests, this type of data modeling combines agile software development approaches, like the Agile Manifesto and Scrum, with the process of data modeling. It aims to develop database architectures that are flexible and responsive to changes in the requirements.
In general, by using this approach, it is possible to refine the data model based on the feedback from end users and evolving business needs. This dynamic method enables your development team to quickly adapt the data model and incorporate new elements.
Learn about the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Practicing the Agile Approach
#10 Temporal Data Modeling
This type of data modeling technique is also known as a historical model. Here again, like the previous one, the name probably speaks highly for itself. Specifically, this model aims to showcase how variables change over time.
Given this, temporal data modeling can be extremely useful to compare historical and current data analysis. This approach can best serve to assess customer behavioral changes and lifecycle. Eventually, it can be dramatically useful for accurate predictive analytics.
If you are looking for robust data modeling tools to streamline data management and visualize variables for better insights, here are the top three options to keep an eye on:
• ER/Studio: Simplifies enterprise-level data model management and visualizes variables.
• ERwin Data Modeler: Optimizes data models for warehouses and manages databases across multiple platforms.
• SQL Database Modeler: Manages popular SQL databases and assists in data visualization.
Common Use Cases of Data Modeling Across Industries
Given all the insights we’ve covered about data modeling so far, you probably see its value and importance. And you’d be right to assume it’s critical for any industry. But let’s skim through the top niches that benefit from data modeling the most.
Healthcare
Data models can assist healthcare providers in many ways. For example, they ensure patient data is stored consistently. Making it possible to analyze users’ behavior and medical history to provide personalized treatment plans and minimize the risk of possible diseases.
Discover how we help the client achieve effective Remote Patient Monitoring
Finance
By picking up the appropriate models, financial institutions can assess credit risk, thus elevating decision-making. Additionally, models can assist in accurately analyzing customer behavior and transaction patterns to promptly identify potential fraudulent activities.
Check out more Opportunities Predictive Analytics Brings to Finance
Retail and eCommerce
Robust demand planning and forecasting are a cornerstone of successful retail and eCommerce businesses. Data modeling can serve best to promptly sort out things. Generally speaking, it organizes sales, customer, and inventory data in a logical and standardized way, which enables more accurate insights and better predictive analytics.
Logistics and Transportation
The relational model can be perfectly useful for this niche. Specifically, you may create columns for order status, shipment, vehicle type, locations, etc., to get real-time updates and effectively organize all the logistics efforts.
Discover how we assist the client in Elevating Cold Chain Monitoring
Telecommunication
The telecom industry can employ data models to monitor network performance and identify possible congestion. Thereby, elevating customer satisfaction and improving operational efficiency.
Best Practices to Create a Solid Data Model
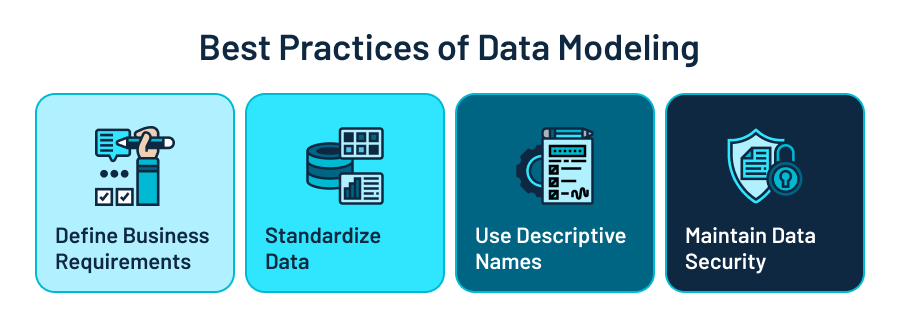
Aiming to get every last drop of your chosen data modeling technique, you need to employ it with best practices in mind. So, what are the fundamental factors to consider for a solid start? Let’s have a look.
- Define business requirements: Without clearly defining your main business objectives, hardly can you pick up a relevant data model.
- Standardize data: When it comes to transforming data into valuable assets, standardization comes to the rescue. By bringing variables into one common format, it highly simplifies data processing and analysis.
- Use descriptive names: To help your team quickly find and efficiently interact with the needed tables and columns, use clear names. This reduces confusion for both your IT and analytics teams.
- Maintain data security: Dealing with data means taking steps to keep it safe. Establishing security measures and defining data governance policies can be highly beneficial to this end.
Leverage Data Modeling for Better Decision-Making
Today, we have discussed top data modeling methodologies and how they are used to drive efficient data engineering and management strategies.
By employing the aforementioned techniques in the right way, you can reap all of their benefits. However, it can be challenging to determine which ones suit your business most and implement them successfully.
If you are not sure what type of data modeling to leverage in accordance with your business needs, our team of data engineers is here to assist you. Don’t hesitate to reach out to us for help.