The shift towards automated manufacturing, powered by advanced technologies, significantly alters traditional production processes. Research reveals that by 2025, manufacturers will automate over half of their tasks. And those taking advantage of IoT stay among the 15% of the top performers.
Thus, technology’s escalating role is no longer a choice but a necessity for businesses striving to stay competitive. The advanced manufacturing software, integration of robotics, artificial intelligence, and cutting-edge machinery is propelling the industry into a new era, eclipsing older methods with unparalleled speed and accuracy.
In this post, we’ll guide you through types of automation in manufacturing, areas where it’s applicable, the business effect of automation, and its future. Join us as we unravel the impact of automation in shaping 21st-century production.
- Application of Automation in Manufacturing
- Types of Manufacturing Automation
- Impact of Automation on Manufacturing
- 12 Tips to Start Automating Things Effectively
Areas in Manufacturing Where Automation Brings Simplicity
In manufacturing, automation simplifies operations across industries and critical areas, making processes more straightforward and smooth. Take assembly lines, for instance. Once reliant on manual labor, automation now handles intricate tasks with robotic attention to detail, delivering a flawless production flow. Let’s take a closer look at this and other areas as well as industry-related examples of automation in manufacturing.
Improved Assembly Precision with Robotic Expertise
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the adoption of automated assembly lines and other advanced automotive technologies. In recent years, major car manufacturers have invested in robotic systems that delicately install complex components, such as sensors and electronic modules.
For example, Tesla’s Gigafactories utilize robotic arms for precision assembly, contributing to improved vehicle quality and production efficiency. This shift results in optimal functionality and reduces human error for manufacturers to enjoy a safer and more cost-effective manufacturing process.
Enhanced Quality Control in Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical manufacturing has also embraced automation for stringent quality control processes. Automated inspection systems, such as machine vision technology, scrutinize pharmaceutical products thoroughly.
A notable example is the use of such inspection systems by Pfizer to detect defects and ensure the highest quality standards in their products. This makes Pfizer a leading pharmaceutical manufacturer known for globally recognized product quality and excellent regulatory compliance with total integrity in their supply chain.
Efficient Material Handling in Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies heavily on automated material handling systems to optimize logistics within manufacturing facilities. Large and delicate components, such as aircraft wings and fuselage sections, are transported using automated guided vehicles and robotic arms.
Boeing’s manufacturing plants are a prime example, where intelligent material handling systems control the movement of components, reduce the risk of damage, and improve the assembly of complex aircraft structures.
Inventory Management in E-commerce
The e-commerce industry has experienced a digital transformation in inventory management through the implementation of automated systems. Amazon, a global e-commerce giant, utilizes advanced data analytics algorithms and robotics in its warehouses to manage inventory levels dynamically.
These systems constantly monitor product demand, adjust stock levels in real time, and optimize order fulfillment processes. The result is a highly responsive supply chain that minimizes stockouts, enhances customer satisfaction, and exemplifies the role of data analytics in modern retail operations.
Read how Velvetech developed an Inventory Management System for a Renewable Energy Company
Precision Machining for Jewelry Manufacturing
CNC automation, which we’ll cover later in the post, has changed precision machining, particularly in industries requiring intricate designs, such as custom jewelry manufacturing.
Companies like Tiffany & Co. utilize CNC machines to craft detailed and complex jewelry pieces with unparalleled accuracy. Thus, they deliver consistent quality and more customized designs. The marriage of precision machining and craftsmanship in this context highlights how technologies drive traditional artistry while meeting the demands of a discerning market.
Efficient Packaging in Food and Beverage
Automation has become an integral solution to error-free packaging processes in the food and beverage industry. The Coca-Cola Company, for instance, employs robotic arms in its bottling plants for packaging operations. These systems handle tasks such as placing caps on bottles and arranging products on packaging lines and contribute to maintaining product consistency across the production line.
Data Analytics for Supply Chain Optimization
Again, automotive manufacturers always stay among the first to adopt new things. They take advantage of data analytics with manufacturing business intelligence software to optimize their complex supply chains. General Motors utilizes advanced analytics to forecast demand, manage inventory levels, and coordinate production schedules. By analyzing vast datasets in real time, GM can make informed decisions, reduce excess inventory, and respond swiftly to market dynamics.
BI for Business
Find out the secrets of how business intelligence boosts operations and what BI tools and practices drive data analysis.
Proactive Maintenance in Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, proactive maintenance through automation has become a cornerstone for the reliability of assets. Vestas, a leading wind turbine manufacturer, employs predictive maintenance strategies that utilize sensors and data analytics software to monitor the condition of turbine components.
By predicting potential issues before they escalate, Vestas can schedule maintenance activities wisely, minimize downtime, and optimize the performance of wind turbines.
Compliance with Document and Customer Management
Pharmaceutical companies, including already mentioned Pfizer, implement document management and CRM systems to stay compliant with regulatory requirements. These systems organize and catalog a vast array of documents, from manufacturing and customer records to regulatory submissions.
The implementation of these facilitates easy retrieval during regulatory inspections and helps build document-centric processes in strictly regulated environments.
Learn about the Advantages of CRM Software for Manufacturers
Better Logistics through Drone Delivery
Retail giants such as Walmart are actively exploring the use of drone delivery systems to improve their logistics. In a pilot program, Walmart utilized drones to deliver selected grocery and household items directly to customers’ homes. An innovative approach to last-mile delivery accelerates delivery times and reduces the carbon footprint associated with traditional vehicles.
The integration of drone technology is reshaping logistics and addressing the evolving expectations of consumers for faster and more sustainable delivery solutions.
Read on How to Develop a Logistics App That’ll Make Things Happen
Sustainable Energy Management with IoT
Finally, smart factories in the manufacturing sector are integrating IoT automation to stay sustainable. Siemens, a multinational conglomerate, employs IoT solutions to monitor and adjust energy consumption in real time across its manufacturing facilities. By aligning energy usage with production needs, Siemens supports judicious resource utilization and reduces environmental impact.
So, these real-world examples from industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and retail demonstrate the tangible benefits of automation in contributing to precision, quality, logistics, and sustainability. As these examples illustrate, often, automation is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, changing industries and setting new standards for operational excellence.
Now, take some time to further explore what types of automation work behind the scenes of the use cases we’ve just described.
Essential Types of Automation in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, automation takes on various forms and configurations, adapting to the diverse scope of tasks you’ve read about earlier, industry standards, and business objectives. This section unveils the most prevalent types of automation and more examples to provide essential insights before making any decisions in this dynamic field.
1. Fixed or Hard Automation
Fixed automation finds its niche in specialized tasks, boosting the high-volume production of standardized products. The ever-innovative automotive industry commits to exactly this type with dedicated assembly lines and robotic welding cells tirelessly building vehicles. This approach reduces labor costs and enhances production speed to meet the consistent demand for standardized products like cars.
2. Programmable Automation
Unlike the previous type, versatility is the hallmark of programmable automation, allowing machines to adapt swiftly to changing requirements. A shining example is in batch production environments, where reprogramming equipment facilitates the creation of different product variations. Here, adaptability ensures efficiency in scenarios where the demand for specific configurations varies over time.
3. Industrial Robotics
As you might notice, the star performers in modern manufacturing are industrial robots, with applications ranging from assembly to welding. Consider another famous example of Amazon’s fulfillment centers, where robotic arms execute precise and rapid material handling tasks. The smooth integration of these robots helps maintain efficient order fulfillment and other warehouse operations.
4. Numerical Control and Computer Numerical Control

NC and CNC represent milestones in the evolution of manufacturing automation. While NC marked the initial move toward automated machining with punched cards, CNC has become the industry standard by leveraging computer technology for better precision, flexibility, and efficiency. CNC has played a pivotal role in modern manufacturing, enabling the production of complex components with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability
5. Flexible or Soft Automation

Adaptability is the bedrock of flexible automation, an extension of the programmable type, addressing the needs of dynamic production environments. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, where products often undergo frequent design changes, flexible automation allows quick reconfiguration to accommodate different formulations. The adaptability delivers responsiveness to market demands and supports agile manufacturing practices.
6. Industrial Automation

Taking a holistic approach, industrial automation integrates sensors, actuators, and control systems for optimized operations. Another Siemens’ Totally Integrated Automation platform is a good example, offering a comprehensive solution that modernizes plants and reduces downtime. One of the strongest impacts of industrial automation is the support of coordination across various manufacturing processes, which makes everything possible.
Explore the Types of IIoT Sensors to Consider for Your Operations
7. Process Automation
Focused on specific tasks within the production workflow, manufacturing process automation software is vital in sectors like chemistry. Control systems are employed to monitor and regulate variables such as temperature and pressure, preserving consistency in product quality. Workflow precision is essential in industries where stringent quality standards must be maintained with less proneness to human error.
Read about how we built an IoT Solution for Cold Chain Management
8. House Automation

Stepping outside the factory, house automation with IoT integrates technology into daily office life. Consider smart thermostats and lighting and security systems that exemplify the principles of automation in households and corporate buildings. Brands like Google and Amazon have propelled the adoption of these technologies, transforming residences into smart, interconnected living spaces.
A prominent trend here is the full integration of IoT mobility. The ability to remotely access and control essential elements simplifies and enhances our lives with increased flexibility. Unsurprisingly, this trend is transitioning into industrial plants as well.
9. Automated Guided Vehicles
In logistics, AGVs are improving material handling in warehouses. Amazon’s use of Kiva robots for order fulfillment exemplifies this. These mobile robots navigate through the warehouse, transporting materials quicker and more accurately. AGVs polish logistics operations, making material transportation more productive than ever.
Read more about Warehouse Optimization with Mobile Technology
10. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
Lastly, at the helm of large-scale operations, SCADA systems offer real-time visibility and control. In industries such as energy, companies gradually shift from cumbersome Excel sheets to new ways of energy inventory management. SCADA systems give tangible help, monitoring and regulating processes to secure optimal performance. This centralized oversight is critical in maintaining efficiency and safety across extensive infrastructural systems.
These types of automated manufacturing signify technological progress and offer practical benefits in terms of productivity, accuracy, and economic growth. While we’ve touched upon specific sectors where these technologies shine, let’s delve deeper into more areas where their application makes the most strategic sense.
How Automated Manufacturing Helps Businesses
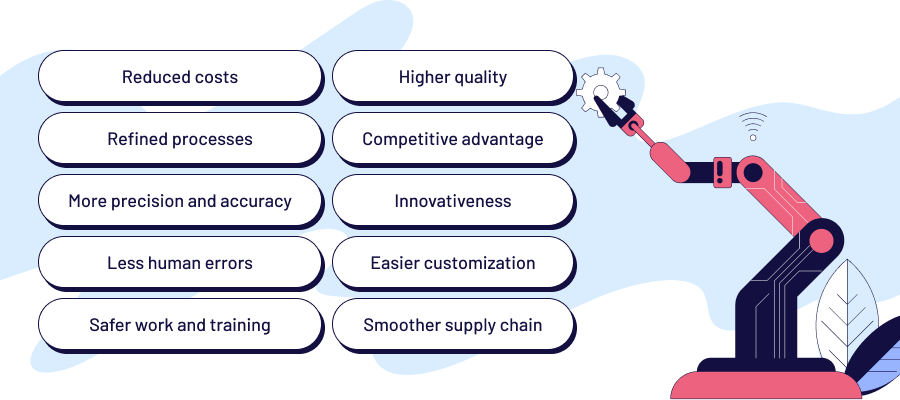
The advent of automated manufacturing has changed production, offering a host of benefits that redefine operational efficiency. This shift not only refines processes but also reduces operational costs, marking traditional manufacturing a thing of the past.
Automated systems excel in precision and consistency, elevating the quality of products to new heights. By minimizing reliance on manual labor, the technology decreases the likelihood of errors, ensuring an uninterrupted workflow. The added safety advantage lies in the ability of machines to handle hazardous tasks, creating a secure working environment and training with such technologies as virtual and augmented reality.
Beyond the shop floor, automation translates into a competitive edge. The swift adaptation to changing production requirements without extensive retooling enables faster time-to-market. It allows businesses to respond promptly to evolving consumer needs. Additionally, automated manufacturing aligns companies with Industry 4.0 standards, like IoT and data analytics integration, positioning them as leaders in technological innovation.
Explore the Reasons to Adopt IoT in Manufacturing
The flexibility of automation extends to customization, enabling businesses to meet individual customer requirements without compromising efficiency. Furthermore, the technology contributes to a more integrated and responsive supply chain and sets up a seamless flow of goods from production to delivery.
Learn about the Top 10 Types of Supply Chain Management Software
In essence, automated manufacturing transcends its utilitarian role, becoming a strategic investment for businesses seeking innovation, efficiency, and sustained success in the global marketplace.
12 Tips to Shift from Traditional to Automated Manufacturing
Transitioning from traditional to automated manufacturing is a journey that demands both time, effort, and a reliable team with an industry-specific skillset. Their expertise should span not only software development but also firmware and hardware engineering, which are integral parts of designing automated systems.
Yet, the payoff is undoubtedly worthwhile. Employ this comprehensive set of tips to facilitate the implementation of your solution, unlocking an era characterized by heightened efficiency and creative excellence:
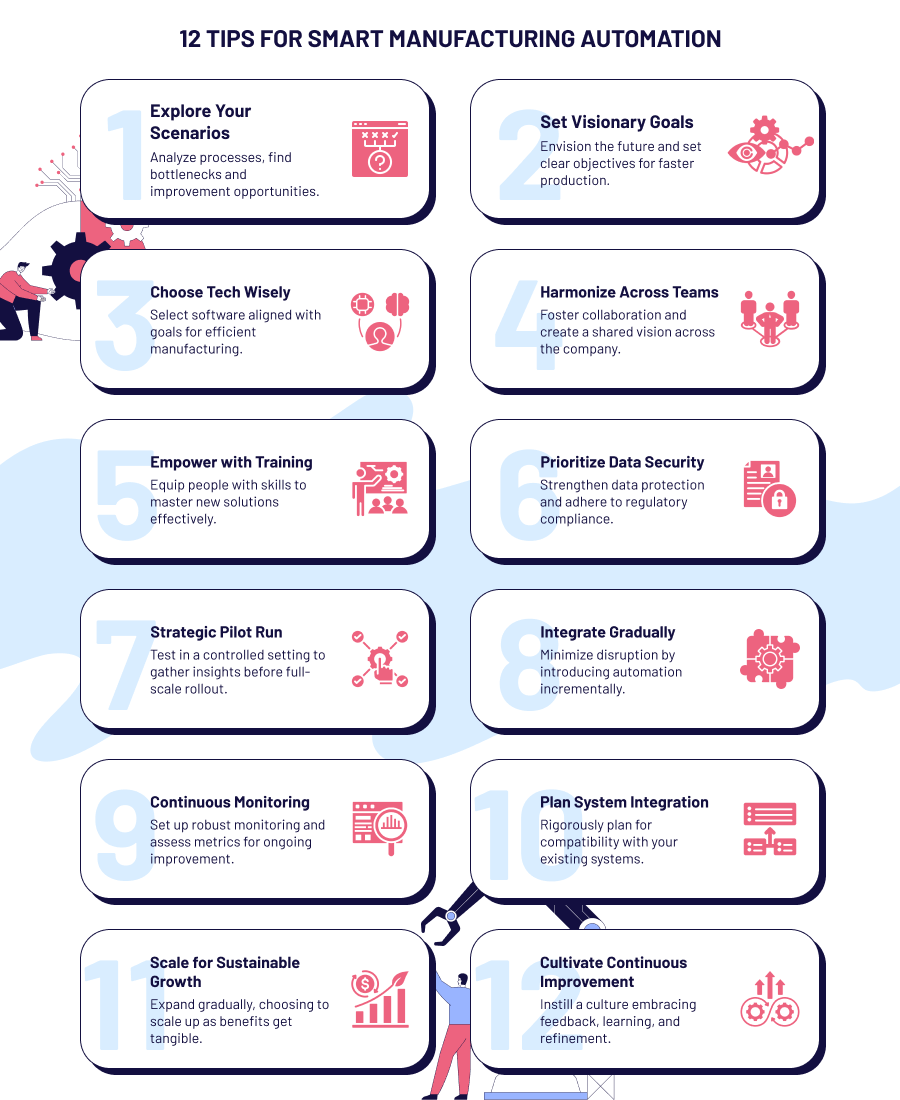
- Deep dive into your manufacturing scenarios. Delve into the intricacies of your current processes and identify bottlenecks ripe for improvement.
- Define visionary goals. Envision the future and set clear, ambitious objectives that resonate with accelerating production.
- Carefully choose your technological ensemble. Select off-the-shelf or build custom software tailored to your industry needs and look for features that align with the goals you set.
- Harmonize across departments. Foster collaboration with stakeholders and other departments to create a collective vision throughout the entire organization.
- Empower with targeted training. Equip your workforce with the skills to navigate the changes and ensure they are not just users but masters of the new solutions.
- Prioritize data security and compliance. Strengthen data protection measures and establish a robust framework to adhere to industry regulations.
- Conduct a strategic pilot run. Test the waters with a pilot phase in a controlled setting. Gather insights, address challenges, and refine the implementation before a full-scale rollout.
- Integrate gradually to minimize disruption. Introduce automation gradually to avoid upheavals. For example, start with selected processes or departments, allowing for a smoother transition.
- Fine-tune with continuous monitoring. Implement a robust monitoring system to track performance. Regularly assess key metrics and make necessary adjustments for ongoing improvement.
- Rigorously plan integration with existing systems. Foster compatibility for a fluid flow of data across platforms.
- Scale step by step for sustainable growth. Expand the implementation gradually as the benefits of automation in manufacturing become evident. Scale up to include additional processes or departments, keeping in mind sustained success.
- Instill a culture of continuous improvement. Foster a culture that embraces continuous refinement. Encourage feedback, learn from challenges, and nurture an environment where everyone contributes to ongoing improvement.
Find out What 16 Key Types of Manufacturing Software Change the Industry
Opt for Automated Not Complicated
As manufacturing undergoes a paradigm shift from traditional to automated processes, companies embracing this transformation enjoy a rich set of benefits. Again, technology is no longer optional but a necessity for businesses striving to remain competitive.
If you’re ready to leverage manufacturing software development or have questions about implementing automation, feel free to reach out to us. Let’s shape a future where your operations excel in efficiency and innovation.