‘Apps’ came into existence in 2007 when the first iPhone was introduced to the public and changed the smartphone industry landscape once and for all. Sure, there were ‘programs’ and ‘applications’, and even ‘software utilities’.
Apps we all know and love to use — with pleasing graphics and smooth animations that turned us into a zombie phone-staring society — definitely appeared together with the first iPhone and later continued spreading to Android and other mobile platforms.
People got so accustomed to using mobile apps in their everyday life that they started asking themselves and their colleagues why they couldn’t use these nice smartphones and tablets for work. That is when enterprise apps started to really pop up.
Users were so obsessed with apps, they were going to give up some of their freedom to be able to solve work-related tasks regardless of where they are: at home, in transit, on vacation or at work. This quickly progressed from thousands to millions, to billions of apps downloaded nowadays.
According to Q4 2022 Data Digest by Sensor Tower, worldwide app downloads totaled 35.5 billion for the quarter.
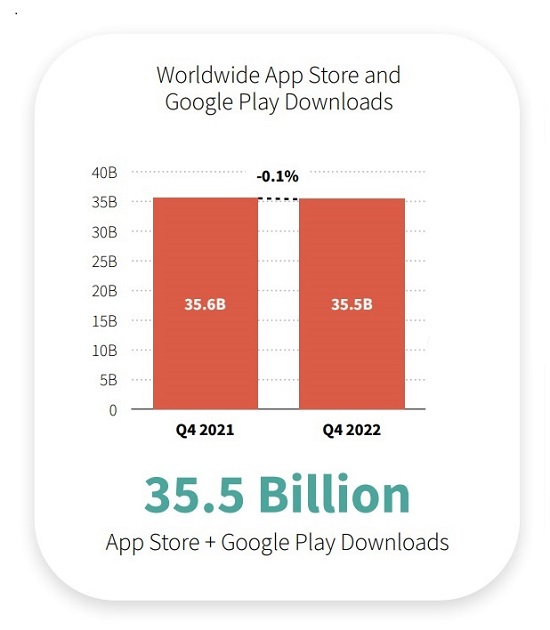
Source: SensorTower
The apps spreading turned out well for both, businesses and users, and brought about enterprise apps to accompany regular consumer-centric apps. Let’s take a closer look at them and check how these two groups compare.
Comparison of Enterprise and Consumer Applications
So as we’ve briefly mentioned, enterprise mobile applications, or business apps, are designed to serve companies and their employees. They support daily operations, streamline workflows, automate processes, and generally enhance performance. For example, such apps are widely used to complement software tools for supply chain management, accounting, CRM, investment, and even to support healthcare professionals.
Read the case study about Investment Management Platform Development
On the other hand, an application built for consumers will have less complex functionality as it’ll have to accommodate more common scenarios. Unlike an app for enterprise goals, a consumer app addresses the needs of individual users, such as communication, entertainment, social networking, shopping, and personal productivity.
All in all, these two groups of mobile solutions differ from the perspective of:
- Target audience
- Accessibility
- Functionalities
- Goals
- Revenue
- Development costs
- Design
Now let’s move to the key considerations you should know while pursuing the development of one of these app categories. Again, we’ll touch upon the differences between enterprise and consumer applications in this section as well.
User-Driven Approach
Watch our webinar and learn the top ways of reducing poor user satisfaction, low adoption rates, and decreased loyalty.
5 Things to Consider When Developing Consumer or Enterprise Mobile Apps
1. UI/UX in Consumer-Centric & Business Apps
Successful consumer apps have stellar graphic design and visually pleasing aesthetics that make people feel great when using them.
These apps take advantage of various features provided by the mobile OSes, such as gestures, widgets, animations, etc. Every user action provides some form of feedback that builds into this positive experience of running a well-designed app.
Enterprise apps focus more on productivity.
Therefore, even though they are heavily influenced by engaging consumer apps with great UI, the design comes second in most enterprise solutions.
In most cases, employees are supposed to use business apps regardless of how they make them feel. This is just how modern businesses operate in recent years.
It should be noted that in some areas where competition is particularly high, e.g. in the CRM software market, businesses are trying to propel their mobile solutions by applying the same design principles as in consumer apps.
Even so, these particular enterprise apps usually lack any custom elements (animations, custom navigation, etc.) and instead stick with so-called native UI/UX building blocks.
“Good design is as little design as possible.”
– Dieter Rams
2. Purpose of Apps: Consumer vs. Business
Consumer apps like Instagram or Bitmoji thrive for the most part because they entertain us. If you check the App Store & Google Play charts, you will see it’s mostly entertainment and social networking apps. In fact, both Apple and Google had to separate games into a different category in their app stores at a certain point to give room for the rest of the apps.
Top Apps by U.S. Downloads
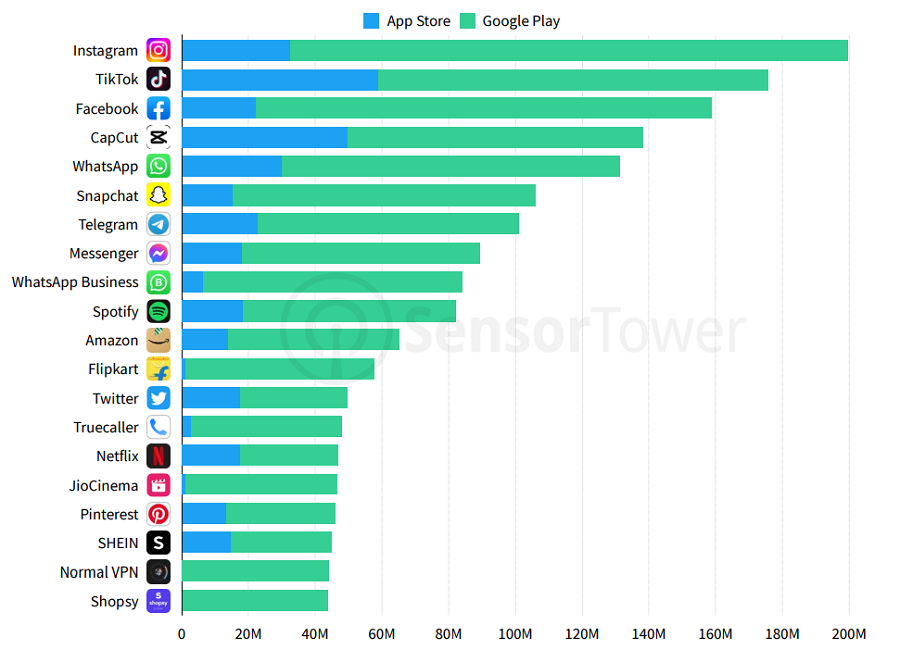
Source: SensorTower
Enterprise apps serve specific business purposes that vary from one company to another. The main goal is that an employee should be able to solve some work-related tasks or make decisions anywhere, anytime.
For example, Salesforce offers its mobile app to unify its collaboration platform Chatter, CRM, custom apps, and business processes into a modern experience. This enterprise app allows sales managers to get their job done and close more deals wherever they are.
Enterprise apps are used by employees within an organization to achieve specific business goals while consumer apps are designed for personal use.
3. Availability of Mobile Apps
Consumer apps are publicly available through App Store and Google Play. There are also many other app stores with Android apps, like Amazon Appstore, Samsung Galaxy Apps, etc.
The idea is that any user with a compatible smartphone can download an app and become its faithful disciple. In fact, companies spend tons of money on App Store Optimization to make sure their apps will get enough user traction and eventually will start turning in some profit.
Learn more about App Store Optimization Tools
Enterprise apps are rarely available through app stores. They are mostly distributed within companies via private repositories and other secure distributing means. On this side of the fence, businesses apply considerable efforts to keep their ‘enterprise apps garden’ secure and safe protecting it with passwords, device-specific profiles, and other security policies.
4. App Development Approach
While consumer apps mostly entertain and deal with trivial info, enterprise ones always operate with businesses’ core data that needs to be secured at all times. Therefore using secure protocols and implementing encryption techniques on top of familiar username and password authentication makes a lot of sense when developing an enterprise app.
Another important point to consider is that business apps will always need to be integrated with some existing web or desktop-based systems that are deployed across the enterprise. This is not always the case with consumer apps that often just sync your data to the cloud for backup but otherwise, are not limited by any legacy systems.
Speaking of the app architecture, enterprise apps are usually more complex than consumer-centric, because of security requirements and integration with legacy solutions. This consequently increases the overall budget for business-related mobile app development.
Find out How to Update Legacy Software
Choosing a Winning App Development Strategy
Watch our webinar to uncover effective mobile development approaches and launch your app.
5. Apps Monetization
Consumer apps generate profit by offering in-app purchases, displaying ads, and selling stuff (as in m-commerce cases). Some of them help establish brand awareness and fulfill similar marketing tasks.
Business apps help reduce the costs of business operations and obviously increase companies’ revenue. However, it is more difficult to assess their share in the overall business profit as it requires deeper analysis compared to checking sales stats for consumer apps.
How would you measure John’s ability to update the CRM on the go after a phone call with a client, so that the lead can proceed further down the sales pipe in the system? Simply said, businesses do not need to monetize their enterprise apps.
Velvetech’s Take On the Topic
We have extensive experience in the development of enterprise apps that allow businesses to effectively solve their tasks. A good example is the Monitoring and Tracking System for Cold Chain which included the development of mobile apps for Android and iOS. These enterprise apps developed by Velvetech became a vital part of the large IoT system successfully deployed at Cargo Data Corporation (Ventura, CA) and today still carry on improving the company’s bottom line.
Some of the consumer apps we work on include an innovative dating app with video profiles and an app for stock trading among others.
We will be happy to hear about your consumer app idea or help you analyze your current business processes and come up with an efficient mobile strategy that will make a positive impact on your business.